The analysis of this genetic data helps researchers expand the understanding of the biology of diseases that affect Singaporeans.
A new study – said to be the largest whole genome sequencing analysis of a diverse Asian population to date – provides valuable insights into the genetic diversity of the varied ethnicity makeup of Singapore’s population. The work is a major stepping stone toward more accurate diagnosis of genetic diseases, advancing research and guiding prevention and targeted therapeutic intervention for chronic diseases.
The study, which is the pilot study of the SG10K project, contains the completely sequenced genomic information of close to 5,000 Singaporeans. The research findings in the paper, “Large-scale whole-genome sequencing of three diverse Asian populations in Singapore”, were published in the scientific journal, Cell, on 17 October 2019. The analysis of the genomic information was done with the aid of the ASPIRE1 petascale supercomputer at the National Supercomputing Centre (NSCC) Singapore.
“Our primary analytics pipelines for joint-calling 4,810 genomes would not have been possible without the supercomputing resources,” said Dr Nicolas Bertin, Programme Manager for National Precision Medicine at A*STAR’s Genome Institute of Singapore. “The success of this project was heavily reliant on access to NSCC resources and as such ensured data and results were delivered on schedule”.
The study was a collaboration among scientists and clinicians from A*STAR’s GIS, National University Health System (NUHS), Singapore Eye Research Institute (SERI), Tan Tock Seng Hospital (TTSH), National Neuroscience Institute (NNI), Khoo Teck Puat Hospital (KTPH), National University Hospital (NUH), SingHealth Duke-NUS Institute of Precision Medicine (PRISM), National University of Singapore (NUS) and Singapore General Hospital (SGH).
To give a scale of some of the supercomputing resources needed, the SG10K pilot project leveraged on nearly 3 million core CPU hours and 1PB of storage provided by NSCC.
NSCC NewsBytes November 2019
*Image credit: Gloria Fuentes – The Visual Thinker LLP
Other Case Studies
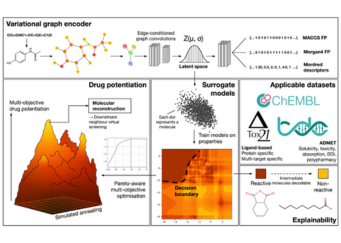
Advancing Drug Discovery Research using NSCC HPC resources
Researchers from Nanyang Technological University (NTU) are applying variational graph encoders as an effective generalist algorithm in computer-aided drug design (CADD)....
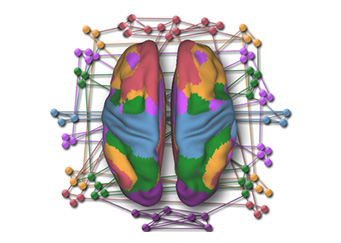
Gaining Deeper Insights into Mental Disorders through Brain Imaging and High-Performance Computing
Researchers from NUS are leveraging supercomputing to develop better strategies for prevention and treatment to mitigate the impact of mental illness. The human brain is a marvel...
Using Digital Twin Technology to Optimise the Industrial 3D Printing Process
Researchers from the Institute of High-Performance Computing (IHPC) are utilizing supercomputers to create a digital twin that furnishes users with comprehensive information...